Kernel Pwn-CISCN 2017 baby driver
Author: 堇姬Naup
基本題,當作入門的第一道題(雖然已經過時了)
前置處理
babydriver.tar 先解壓縮
1 | tar -xvf babydriver.tar |
裡面有三個文件
boot.sh : 啟動腳本
bzImage : kernel映像檔
rootfs.cpio : 文件系統
文件系統
先extract文件系統,將cpio提取到sysfile底下
1 | mkdir -p sysfile |
boot.sh
啟動腳本,可以用來創建qemu虛擬環境
1 | #!/bin/bash |
init file
啟動時候會用inmod將babydriver.ko載入
LKM(Loadable kernel module)可以想像他是插件的概念,用來擴充kernel的功能
1 | insmod 載入LKM |
並且將flag設為400,也就是只有root才能讀到,要做提權
1 |
|
IDA分析
既然他載入了babydriver(driver可以想像是與硬體設備的接口,可以與硬體做交互,包括open、read、write、…),那就去分析他
babydriver_init()
簡單來說會做一些簡單的初始化,並建立一個設備,/dev/babydev
1 | __int64 __fastcall babydriver_init() |
babydriver_exit()
刪除一個設備 /dev/babydev
1 | void __fastcall babydriver_exit() |
babyopen()
用kmem_cache_alloc_trace分配一塊記憶體,簡單來說就是打開這個設備,可以對這個設備做操作
1 | __int64 __fastcall babyopen(inode *inode, file *filp, __int64 a3, __int64 a4) |
babyrelease()
用kfree釋放掉打開的dev
1 | __int64 __fastcall babyrelease(inode *inode, file *filp, __int64 a3, __int64 a4) |
babyread() & babywrite()
實現了user mode跟kernel對dev的溝通及互動
1 | size_t __fastcall babyread(file *filp, char *buffer, size_t length, loff_t *offset) |
1 | size_t __fastcall babywrite(file *filp, const char *buffer, size_t length, loff_t *offset) |
babyioctl()
如果command 是 65537,那會先free掉原先的device buffer,然後重新kmalloc一塊給device buffer
1 | __int64 __fastcall babyioctl(file *filp, __int64 command, unsigned __int64 arg, __int64 a4) |
cred struct
https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.4.72/source/include/linux/cred.h#L118
1 | struct cred { |
如果有下過id這個指令,會發現root的uid跟gid都是0,而他是由cred結構進行管理,若我們能將cred的uid跟gid改成0,再開一個進程,就可以提權到root
漏洞
如果再usermode中,看起來沒什麼問題
但是在kernel中,設備是共享的,你可以對同一台設備打開兩次,接著free掉其中一個,這時候如果沒有清空pointer(babydev_struct他是一個全域變數),就會造成UAF
用ioctl可以重新分配chunk大小,將chunk改為0xa8,也就是cred struct大小
接下來如果我開一個新的process,會malloc一個cred struct(size 0xa8),並且該塊會拿到你之前free chunk,此時將cred內的值(gid、uid)蓋為0,就可以提權到root了
script
編輯exploit到sysfile底下的tmp中,之後重新打包cpio,這樣qemu模擬時就可以一併把你的腳本包進去
1 | find . | cpio -o --format=newc > ../rootfs.cpio |
記得要加wait,不加會爛掉,猜測是因為父進程先結束掉了,所以加入wait等待子進程結束
1 |
|
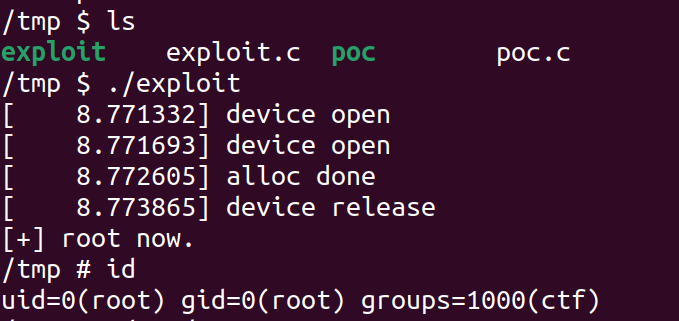
成功提權