Pwnable.tw-BookWriter
Author: 堇姬Naup
libc
glibc all in one 中沒有 2.23-0ubuntu5
所以去網路上找libc
https://launchpad.net/ubuntu/xenial/amd64/libc6/2.23-0ubuntu5
把amd64載下來
1 | dpkg -X libc6_2.23-0ubuntu5_amd64.deb . |
在libs裡面就有ld跟libc了
patchelf直接patch上去
1 | patchelf --set-interpreter ld-2.23.so bookwriter |
IDA分析
main
1 | void __fastcall __noreturn main(int a1, char **a2, char **a3) |
Author
1 | __int64 Author() |
輸入一個Author,大小為0x40
menu
1 | int menu() |
有四種功能
ADD
1 | int ADD() |
VIEW
1 | int VIEW() |
EDIT
1 | int EDIT() |
INFOR
1 | unsigned __int64 INFOR() |
分析
leak libc & leak heap
author緊鄰heap arr,可以用來leak heap,直接info收就可以了
1 | .bss:0000000000602060 input_author db 40h dup(?) ; DATA XREF: Author+18↑o |
接下來edit中長度控制是從size arr中獲得的
但是size arr會在每次edit時候根據strlen heap arr去做修改,然而當我把prev size覆蓋掉時,top chunk size就會被算進去,這樣導致heap overflow
1 | read_f((__int64)(&heap_arr)[v1], size_arr[v1]); |
這邊就可以打 house of orange了
當我們malloc大小大於top chunk剩餘空間,且FastBin、SmallBin、LargeBin、UnsortedBin都不能找到可以對應的空間時候,ptmalloc會調用brk/mmap申請一塊新的空間,原來的top chunk會被加到unsorted bin中
不過有以下限制
- malloc chunk size < mmp_.mmap_threshold (默認128KB,也就是0x20000),不然會直接syscall mmap
- Top Chunk size要對齊page(0x1000)
- Top chunk size > MINSIZE(0x10)
- Top Chunk的Size < malloc chunk size + MINSIZE
- Top Chunk Size Pbit = 1
然而要達成這條件實際上可以透過只修改高位top chunk size來bypass
0x20fd1 -> 0xfd1
在malloc 0x1000
就可以拿到一塊unsorted bin了
然而我這樣做就爛了,原因是因為只要有輸入就會自動補一個NULL bytes,原來是因為read function會把\n改成\x00
我們可以透過malloc 0x0來bypass
1 | from pwn import * |
RCE
因為沒有free,就繼續打house of orange
來回顧一下house of orange
unsorted bin attack
首先是先了解unsorted bin attack
可以參考Pwn-heap note 1的部分
https://hackmd.io/4fsviCDBQqG_aTIeq1fcMw?view#unsorted-bin-attack
IO_FILE
先來關注malloc_printerr
https://elixir.bootlin.com/glibc/glibc-2.23/source/malloc/malloc.c#L4987
1 | static void |
他主要調用了__libc_message
跟進去看
https://elixir.bootlin.com/glibc/glibc-2.23/source/sysdeps/posix/libc_fatal.c#L67
這邊可以看到他最後調用了abort來kill整個process
1 | if (do_abort) |
重點關注abort這裡
https://elixir.bootlin.com/glibc/glibc-2.23/source/stdlib/abort.c#L50
1 | if (stage == 1) |
調用flush 實際上調用 _IO_fflush
https://elixir.bootlin.com/glibc/glibc-2.23/source/libio/iofflush.c#L31
_IO_fflush 調用 _IO_flush_all 調用 _IO_flush_all_lockp
https://elixir.bootlin.com/glibc/glibc-2.23/source/libio/genops.c#L814
https://elixir.bootlin.com/glibc/glibc-2.23/source/libio/genops.c#L759
他會從 _IO_list_all 開始循環,將當前循環的fp作為
_IO_OVERFLOW (fp, EOF) 參數傳入
1 | int |
看到這裡應該可以發現如果能偽造 IO_list_all上的IO_FILE,就可以控制程式
另外也可以劫持 IO_list_all,來做FSOP
結合前面的 unsorted bin可以在任意 address寫上一個main arena address,所以我們將 IO_list_all寫上 main arena位置,此時的main arena被當 IO_FILE(然而main arena不可控)
1 | 'amd64':{ |
offset = 0x68的位置是 _chain,他會指向下一塊IO_FILE,如果能把它指向 heap chunk,那就可以打偽造一塊完整的 IO_FILE 來RCE
那要如何讓 _chain變成heap chunk address呢?
關注一下main arena
unsorted bin後面的 62 塊chunk均為 small bins
small bins 內的chunk 如下
| bins | chunk size(32bits) | chunk size(64bits) |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 16 | 32 |
| 3 | 24 | 48 |
| 4 | 32 | 64 |
| x | 8*x | 16*x |
| 63 | 504 | 1008 |
目前_chain 指向 main arena + 88 + 0x68 = main arena + 0xc0 這是一個small bin,將small bin的chunk偽造,頭部改成/bin/sh\x00,vtable的IO_OVERFLOW改system
透過觸發malloc err來觸發

接下來我們回到題目上
我要使用house of orange那我應該如何去寫unsorted bin呢
因為我們現在是沒有一個heap overflow可以去寫到unsorted bin的fd bk
觀察一下IDA跟gdb
會發現heap array長度是8,緊接著是size array,但是他循環了9次可以malloc,所以可以溢出寫size array,讓size變成一個很大的數字
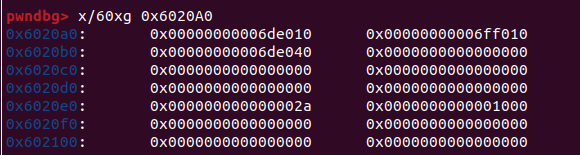
第一塊chunk就會有超級大的溢出
我們把原本top chunk變成unsorted bin的那塊prev size改為/bin/sh
size 蓋成 0x60
剩下的就按照house of orange蓋法,之後蓋掉vtable pointer到fake file下方,並偽造第4個為system
之後去處發malloc error,原本的unsorted bin那塊0x60,會進到small bin,_IO_list_all會被蓋成main arena
small bin 0x60會是_chain,剛好只到0x60那塊
malloc err在flush,就會IO_overflow(small_bin_fp(指向/bin/sh))
-> system(‘/bin/sh’)
不過我腳本不是百分百成功,不知道為甚麼
exploit
1 | from pwn import * |
